
Conscious Capitalism: Liberating the Heroic Spirit of Business by John Mackey and Raj Sisodia is more than just a book. It’s a manifesto for reimagining the role of business in society. Mackey and Sisodia co-founded the Conscious Capitalism movement. They present a compelling case for why capitalism, when practiced consciously, can be a force for good. This post delves into the key insights and principles of this groundbreaking book. It offers takeaways in a comprehensive analysis for business leaders, entrepreneurs, and anyone interested in the future of ethical business practices.
What is Conscious Capitalism About?
The book challenges the traditional narrative that businesses exist solely to maximize profits. Instead, Mackey and Sisodia argue that businesses have a higher purpose. They aim to create value for all stakeholders. These include customers, employees, suppliers, investors, society, and the environment. The authors provide real-world examples from companies like Whole Foods Market, Patagonia, Google, and Costco. They show how conscious businesses thrive when they align profit with purpose.
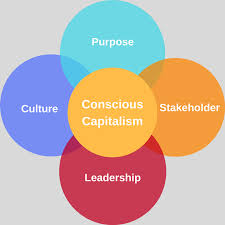
The book is built on four key tenets:
- Higher Purpose: Businesses should aim to make a positive impact on the world, beyond just generating revenue.
- Stakeholder Integration: Companies must consider the needs of all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
- Conscious Leadership: Leaders should inspire and empower their teams, fostering a culture of trust and collaboration.
- Conscious Culture and Management: A values-driven culture is essential for long-term success.
Why Conscious Capitalism Matters
Consumers increasingly demand ethical and sustainable practices in today’s era. Conscious Capitalism offers a roadmap for businesses to thrive while making a positive impact. The book urges leaders to adopt a more evolved form of capitalism. This form prioritizes people and the planet alongside profit.
Key takeaways include:
- Business as a Force for Good: The authors argue that business is inherently good. It creates value. It fosters innovation. It lifts people out of poverty.
- The Power of Purpose: Companies with a clear higher purpose outperform their competitors and enjoy greater employee and customer loyalty.
- Long-Term Thinking: Conscious businesses focus on long-term value creation rather than short-term gains.
Real-World Examples of Conscious Capitalism
Mackey and Sisodia highlight several companies that embody the principles of Conscious Capitalism:
- Whole Foods Market: Prioritizes organic and sustainable products, fair wages, and employee empowerment.
- Patagonia: Champions environmental sustainability and ethical supply chains.
- Google: Focuses on innovation and creating value for users while maintaining a strong corporate culture.
- Costco: Offers fair wages and benefits to employees, fostering loyalty and reducing turnover.
These companies prove that conscious business practices are not only ethical but also profitable.
Criticism and Counterarguments
Conscious Capitalism has been widely praised. However, some critics argue that the principles may be difficult to implement in highly competitive industries. These principles could also be hard for smaller businesses with limited resources. Others question whether the movement is scalable or if it risks being co-opted by companies for PR purposes. However, Mackey and Sisodia address these concerns by emphasizing a crucial point. Conscious practices are a journey, not a destination. They stress that even small steps can lead to meaningful change.
Who Should Read This Book?
- Business Leaders: Learn how to align your company’s mission with a higher purpose.
- Entrepreneurs: Discover how to build a values-driven business from the ground up.
- Students and Academics: Gain insights into the future of ethical business practices.
- Consumers: Understand how your purchasing decisions can support conscious businesses.
Comparison Table: Conscious Capitalism vs. Traditional Capitalism
| Aspect | Conscious Capitalism | Traditional Capitalism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Creating value for all stakeholders (customers, employees, suppliers, society, environment). | Maximizing profits for shareholders. |
| Purpose | Higher purpose: Businesses exist to make a positive impact on the world. | Profit-driven: Businesses exist primarily to generate financial returns. |
| Stakeholder Approach | Stakeholder integration: Balances the needs of all stakeholders. | Shareholder primacy: Prioritizes the interests of shareholders. |
| Leadership Style | Conscious leadership: Emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and long-term thinking. | Transactional leadership: Focuses on short-term results and efficiency. |
| Culture | Conscious culture: Values-driven, fosters trust, transparency, and employee well-being. | Competitive culture: Often prioritizes performance metrics over employee morale. |
| Decision-Making | Long-term perspective: Considers the broader impact of decisions on society and the environment. | Short-term focus: Decisions are often driven by quarterly earnings and immediate gains. |
| View of Profit | Profit as a means to achieve a higher purpose and create value. | Profit as the primary goal and measure of success. |
| Ethical Considerations | Strong emphasis on ethics, sustainability, and social responsibility. | Ethics and sustainability are often secondary to financial performance. |
| Examples of Companies | Whole Foods Market, Patagonia, Costco, Google, The Container Store. | Many traditional Fortune 500 companies focused on shareholder returns. |
| Impact on Society | Aims to lift people out of poverty, create prosperity, and protect the environment. | May contribute to economic growth but can exacerbate inequality and environmental degradation. |
| Employee Treatment | Prioritizes fair wages, benefits, and employee empowerment. | Often focuses on cost-cutting, which can lead to lower wages and job insecurity. |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation that aligns with societal and environmental needs. | Innovation is primarily driven by market competition and profit motives. |
| Criticism | May be seen as idealistic or difficult to implement in highly competitive industries. | Criticized for fostering inequality, environmental harm, and short-termism. |
Key Takeaways
- Conscious Capitalism redefines the role of business by emphasizing purpose, stakeholder well-being, and long-term value creation.
- Traditional Capitalism focuses on profit maximization and shareholder returns, often at the expense of other stakeholders.
- Both models have their merits. However, Conscious Capitalism offers a more sustainable approach. It also provides an ethical approach to business in the 21st century.
This comparison highlights the transformative potential of Conscious Capitalism. It addresses the limitations of traditional capitalism. This approach creates a more equitable and sustainable future.
Final Thoughts
Conscious Capitalism: Liberating the Heroic Spirit of Business is essential for readers. It appeals to those who believe in the power of business to create positive change. Mackey and Sisodia’s vision of a more humane and sustainable form of capitalism is both inspiring and actionable. By embracing the principles outlined in this book, businesses can achieve financial success. They can also contribute to a better world.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of Conscious Capitalism?
You can purchase Conscious Capitalism: Liberating the Heroic Spirit of Business on Amazon. Start your journey toward building a more ethical and impactful business today!
Deja un comentario